Streaming Media
Resolution, Aspect Ratio and Orientation
Resolution
Resolution means the native resolution of the camera (input). In the most situations this will be the same for the output.
To set the resolution there is a function in the VideoSettings object called setResolution(Resolution res). If you set a resolution that the
device doesn't support, nanoStream will automatically switch to the nearest resolution available on the device. A list of supported resolutions for the current video source can be obtained from getCapabilities().listAvailableVideoResolutions()
on the nanoStream object.
Aspect Ratio
Aspect ratio means the aspect ratio of the outgoing stream. The aspect ratio determines if the input video needs to be cropped.
The aspect ratio can be set through the setAspectRatio(AspectRatio aspectRatio) function on the VideoSettings object.
Supported Aspect Ratios
| Aspect Ratio | AspectRatio value |
|---|---|
Keep Input | AspectRatio.RATIO_KEEP_INPUT |
1:1 | AspectRatio.RATIO_1_1 |
4:3 | AspectRatio.RATIO_4_3 |
16:9 | AspectRatio.RATIO_16_9 |
3:4 | AspectRatio.RATIO_3_4 |
9:16 | AspectRatio.RATIO_9_16 |
Orientation
The default stream orientation is landscape. If you switch to portrait the resolution will swap width and height, e.g. from 640x480 to 480x640.
You can set the stream orientation on the nanoStream object with the setStreamRotation function. The stream orientation needs to be set
before starting the stream, it is not possible to switch the orientation during the stream.
Supported Orientations
| Orientation | Rotation Value |
|---|---|
Landscape | Rotation.ROTATION_0 |
Portrait | Rotation.ROTATION_90 |
Landscape Upside Down | Rotation.ROTATION_180 |
Portrait Upside Down | Rotation.ROTATION_270 |
Example Combinations of Aspect Ratios and Orientations
The input resolution is set to 640x480 here.
The red rectangle marks up the active area that is included in the output stream.
| Orientation | Aspect Ratio | Stream Area |
|---|---|---|
| Portrait1 | Keep Input |  |
| Portrait1 | 4:3 | 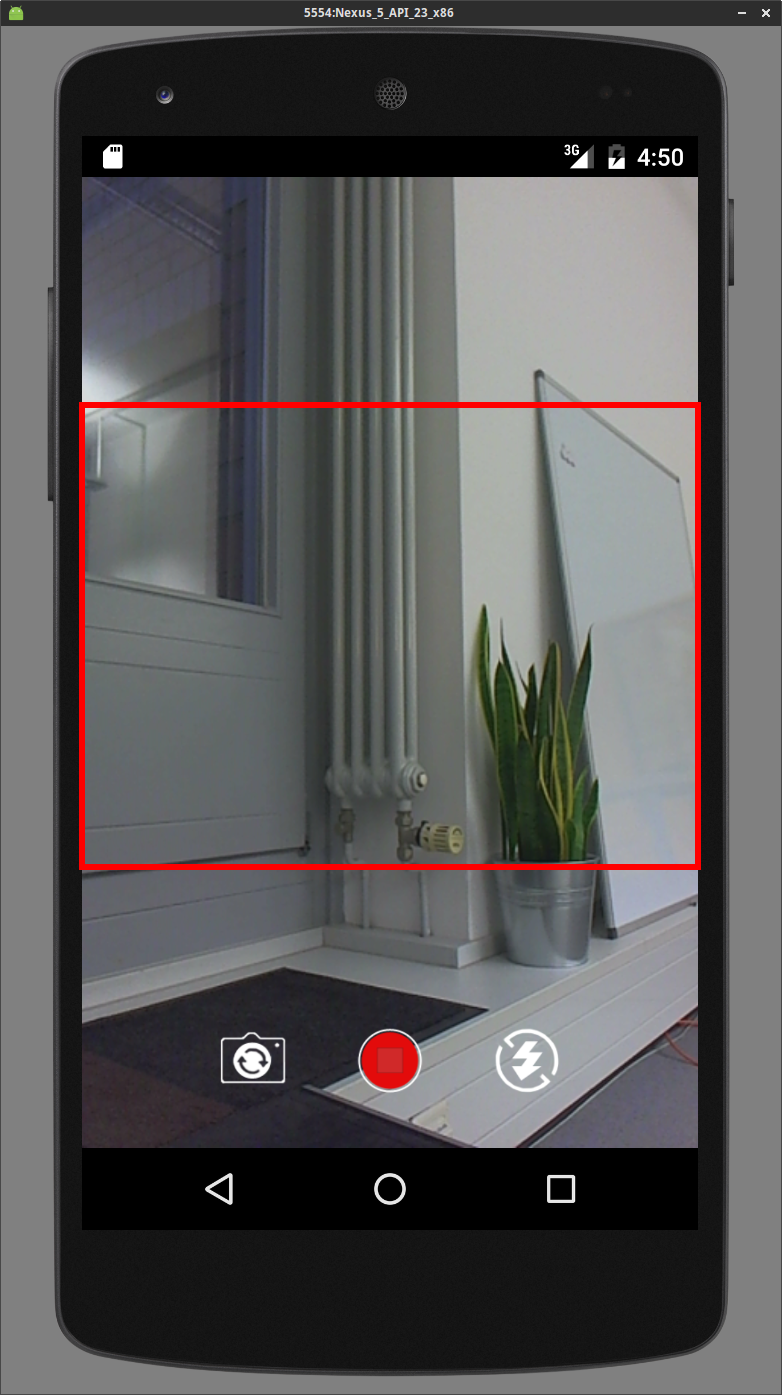 |
| Portrait1 | 3:4 |  |
| Portrait1 | 16:9 | 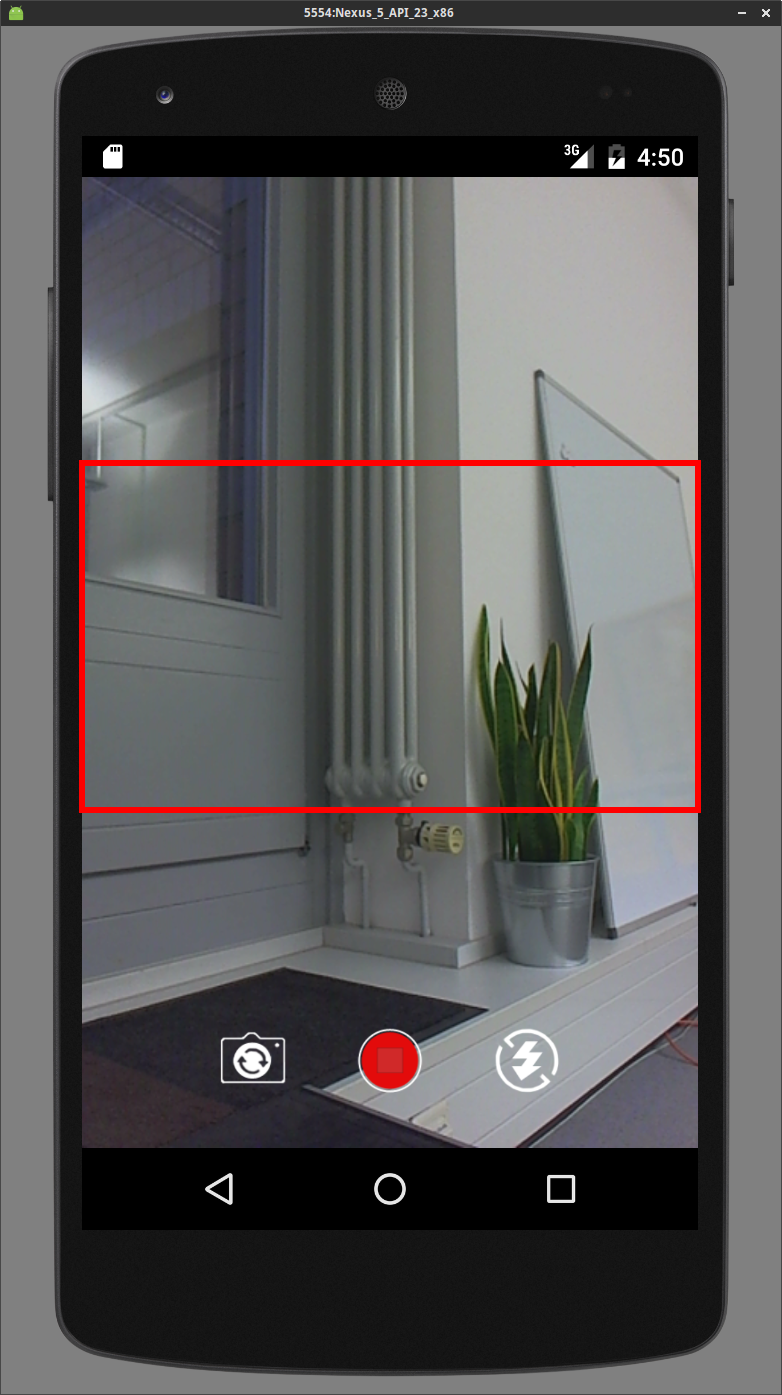 |
| Portrait1 | 9:16 |  |
| Landscape | Keep Input |  |
| Landscape | 4:3 |  |
| Landscape | 3:4 |  |
| Landscape | 16:9 |  |
| Landscape | 9:16 |  |
Example
If you want to stream with a resolution of 640x360 but your device doesn't supports this resolution, you need to crop the resolution from 640x480 (this resolution is supported by the most devices) to 640x360.
This can be done through the aspect ratio, so you need to set the aspect ratio to 16:9 to stream with a resolution of 640x360.
Implementation Example
public class MainActivity {
...
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
nanoStreamSettings nss = new nanoStreamSettings();
VideoSettings vs = new VideoSettings();
...
vs.setResolution(new Resolution(640, 480)); // default value
vs.setAspectRatio(AspectRatio.RATIO_16_9); // default value is AspectRatio.KEEP_INPUT
...
streamLib = new nanoStream(nss);
streaLib.init();
streamLib.setStreamRotation(Rotation.ROTATION_0); // default value
...
}
...
}
Stream Type
The SDK supports differnet streaming modes:
- Video and Audio
- Video only
- Audio only
You can en/disable Video/Audio in the nanoStreamSettings.object
Implementation Example
nanoStreamSettings nss = new nanoStreamSettings();
nss.setHaveVideo(true); // false
nss.setHaveAudio(true); // false
Server Authentication
In case authentication is required, the credentials can be set on the nanoStreamSettings object.
Implementation Example
nanoStreamSettings nss = new nanoStreamSettings();
nss.setAuthUser("user");
nss.setAuthPassword("password");
Local Recording
Description
The nanoStream Android SDK supports local file recording on the device in MP4 format. This document describes how to enable and configure nanoStream for local recording.
Steps to configure MP4 recording
MP4 recording can be configured with two function calls on a nanoStreamSettings object.
- Enabling MP4 recording:
setRecordMp4(boolean) - Setting up the file path:
setMp4Path(String)
setRecordMp4(boolean)
The setRecordMp4 function takes a boolean as parameter to enable/disable the recording function.
setMp4Path(String)
The setMp4Path function takes a String as parameter. This string needs to be a valid file path (e.g. /sdcard/test.mp4). It is recommended to use the getExternalStorageDirectory or getExternalStoragePublicDirectory functions from the [Android Enviroment][8928e181] API, and add a file name to the returned path. Please find the code snippet below as an example.
Android Permission
To be able to write to an external file path your Android app needs the following permissions to be added to the app manifest (AndroidMainfest.xml).
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.STORAGE" />
Android 6.0
Due to the new permission handling in Android 6 (M) writing to external directories (DCIM) requires a permission by user. Writing to the applications own data directory (/Android/data/com.companyname.appname/) is not restricted.
Implementation Example
File externalFilePath = Environment.getExternalStoragePublicDirectory(Environment.DIRECTORY_DCIM);
File filePath = new File(externalFilePath, "myMp4File.mp4");
String mp4FilePath = filePath.getAbsolutePath();
nanoStreamSettings nss = new nanoStreamSettings();
nss.setRecordMp4(true);
nss.setMp4Path(mp4FilePath);
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
By using the Adaptive Bitrate Control (ABC) the stream will automatically adjust to changes of the bandwidth. There are four modes available:
DISABLED: The Adaptive Bitrate Control is disabled.QUALITY_DEGRADE: The video quality will be changed if the bandwidth changes. For instance, if not enough bandwidth is available, the video bitrate will be decreased, which in turn degrades the video quality.FRAME_DROP: Low bandwidth is compensated by decreasing the framerate (FPS), but maintaining the video qualtiy.QUALITY_DEGRADE_AND_FRAME_DROP: The video quality and the framerate (FPS) decreased if the not enough bandwidth is available.
Make sure to set the ABC settings before a stream is started.
Implementation Example
private AdaptiveBitrateControlSettings.AdaptiveBitrateControlMode abcMode = AdaptiveBitrateControlSettings.AdaptiveBitrateControlMode.QUALITY_DEGRADE_AND_FRAME_DROP;
private int videoBitrate = 500000;
private void initStreamLib() {
AdaptiveBitrateControlSettings abcSettings = new AdaptiveBitrateControlSettings(abcMode);
abcSettings.SetMaximumBitrate((int)(videoBitrate * 1.5));
nanoStreamSettings nss = new nanoStreamSettings();
nss.setAbcSettings(abcSettings);
}
Measuring the available bandwidth
For measuring the available bandwidth you can use the method runBandwidthCheck. After the check finished, the result can be used to set the bitrate for the nanoStream object.
The check measures the bandwidth by running a test stream to the server.
The BandwidthCheck Class has three public functions:
runBandwidthCheck(BandwidthCheckSettings settings, BandwidthCheckResultCallback callback())forceStop()abort()
There is a BandwidthCheckSettings Class, the constructor creates a standard object of BandwidthCheckSettings, with the following settings:
| property | default values | meaning |
|---|---|---|
prerollSeconds | 1 (in sec.) | this is the pre roll time to connect to the server |
runTime | 5 (in sec.) | the run time of the bandwidth check |
maxBitrate | 3000000 (bit/s = 3 MBit/s) | the maximum bit rate for the bandwidth check |
rtmpUrl | empty | the rtmp url for the bandwidth check |
streamId | empty | the stream id for the bandwidth check |
With this settings you can call the runBandwidthCheck methode, the second parameter is the callback for the results. This callback class has a finished method that will be called after bandwidth check is done. The finished method has one parameter from type BandwidthCheckResult, this object has 6 getter methods:
getAverageBitrate()// the average measured bandwidthgetMedianBitrate()// the median measured bandwidthgetMaxBitrate()// the maximum measured bandwidthgetMinBitrate()// the minimum measured bandwidthgetRunTimeMS()// the run time in msgetErrorCode()// the error code if all is ok this is nanoResults.N_OK (all error codes can be found in the nanoStream API Reference documentation for nanoResults)
The forceStop call stops the bandwidth check and will return the results that where measured until then. The abort call stops the bandwidth check but don't return any results.
The bandwidth check, sends a special type of metadata that will not be recorded on the Streaming Server.
Implementation Example
private BandwidthCheck bwCheck = null;
private class CustomBandwidthCheckResultCallback implements BandwidthCheckResultCallback {
@Override
public void finished(final BandwidthCheckResult bandwidthCheckResult) {
Log.d(TAG, "BandwidthCheck results: " +
"\n\tAverage Bitrate (kBit/s): " + bandwidthCheckResult.getAverageBitrate() / 1000 +
"\n\tMedian Bitrate (kBit/s): " + bandwidthCheckResult.getMedianBitrate() / 1000 +
"\n\tMax Bitrate (kBit/s): " + bandwidthCheckResult.getMaxBitrate() / 1000 +
"\n\tMin Bitrate (kBit/s): " + bandwidthCheckResult.getMinBitrate() / 1000 +
"\n\tRun Time (ms) : " + bandwidthCheckResult.getRunTimeMS());
}
}
private void initBandwidthCheck() {
if(null == bwCheck) {
BandwidthCheckSettings settings = new BandwidthCheckSettings();
settings.setRtmpUrl(serverUrl);
settings.setStreamId(streamName);
bwCheck = new BandwidthCheck();
bwCheck.runBandwidthCheck(settings, new CustomBandwidthCheckResultCallback());
}
}
##Snapshot
To get a snapshot (image) of the current preview/stream, the method takeSnapshot can be used. This is a non blocking function, for the result you need to implement the SnapshotCallback interface. The snapshot returns as a base64 encoded JPEG
Implementation Example
private class CustomSnapshotCallback implements SnapshotCallback {
@Override
void onSuccess(String arg0){
// do something with the base64 encoded JPEG.
}
@Override
void onFailure(){
Log.d(TAG, "takeSnapshot() failed!")
}
}
private void shapshot() {
streamLib.takeSnapshot(new CustomSnapshotCallback());
}
Camera Zoom
Description
The nanoStream Android SDK supports camera zoom, if the internal camera supports it. Therefor there are a few functions, the most important are:
| Function | Return Type | returns |
|---|---|---|
hasZoom() | boolean | true if zoom is supported by the video source/ device |
getZoomRatios() | List<Integer> | list with of ale zoom ratios |
getZoom() | int | the index of the List<Integer> that returned from getZoomRatios() |
setZoom(int) | int | the new index of the List<Integer> that returned from getZoomRatios() |
It is recommended to use pinch to zoom, therefor you need to implement a ScaleGestureDetector.SimpleOnScaleGestureListener, and a pinch2zoom function, that takes the scalefactor from the SimpleOnScaleGestureListener as a int parameter, take a look at the [Implementation Example][ef1c8421].
getZoomRatios()
getZoomRatios() returns a List of Integer values, this values are the zoom ratios in 1/100 increments (e.g. a zoom of 3.2x is returned as 320).
setZoom(int)
The int parameter from setZoom(int zoom) is the index of zoom ratios that returns getZoomRatios().
Zoom Behavior on Camera Switch
During a camera switch (e.g. from back to front) the zoom remains unaffected.
Implementation Example
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private ScaleGestureDetector scaleGestureDetector;
private List<Integer> mZoomRatios = null;
private nanoStream streamLib = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
nanoStreamSettings nss = new nanoStreamSettings();
// configure nanoStreamSettings
streamLib = new nanoStream(nss);
if(streamLib.hasZoom()) {
mZoomRatios = streamLib.getZoomRatio();
}
if(null == scaleGestureDetector) {
scaleGestureDetector = new ScaleGestureDetector(this, new ScaleGestureListener());
}
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)
{
if (scaleGestureDetector != null)
{
scaleGestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
}
return true;
}
private class ScaleGestureListener extends ScaleGestureDetector.SimpleOnScaleGestureListener {
@Override
public boolean onScale(ScaleGestureDetector detector) {
if(null != streamLib) {
if (streamLib.hasZoom()) {
pinch2Zoom(detector.getScaleFactor());
}
}
return true;
}
}
public void pinch2Zoom(float scaleFactor) {
if (streamLib.hasZoom() && null != mZoomRatios) {
int zoomFactor = streamLib.getZoom();
float zoomRatio = mZoomRatios.get(zoomFactor) / 100f;
zoomRatio *= scaleFactor;
if (zoomRatio > 1.0f) {
if (scaleFactor > 1.0f) {
for (int i = zoomFactor; i < mZoomRatios.size(); i++) {
Double zoom = mZoomRatios.get(i) / 100.0;
if (zoom >= zoomRatio) {
streamLib.setZoom(i);
break;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = zoomFactor; i > 0; i--) {
Double zoom = mZoomRatios.get(i) / 100.0;
if (zoom <= zoomRatio) {
streamLib.setZoom(i);
break;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
Camera Focus
Description
The nanoStream Android SDK supports camera focus and focus lock, if the internal cameras supports them. There are two non-blocking functions
setFocusArea(int focusWidth, int focusHeight, float areaMultiple, int x, int y, int previewWidth, int previewHeight, int weigh)
setFocusLockArea(int focusWidth, int focusHeight, float areaMultiple, int x, int y, int previewWidth, int previewHeight, int weigh)
through the
addFocusCalback(FocusCallback callback)
removeFocusCalback(FocusCallback callback)
you can attach or remove a FocusCallback listener.
To check if your device supports focus call the function
isFocusSupported()
which will return true or false.
Parameter List
| Parameter name | meaning |
|---|---|
focusWidth | the focus Area width |
focusHeight | the focus Area height |
areaMultiple | a Multiple for the focus area (default: 1f) |
x | the x position on the Screen |
y | the y position on the Screen |
previewWidth | the width of the preview |
previewHeight | the height of the preview |
weight | the weight of the area must be range from 1 to 1000 |
FocusCallback interface
The FocusCallback interface has three abstract functions
onSuccess()
onSuccess(Rect rect, Boolean focusLock)
onFailure()
Implementation Example
public class MainActifity extens Actifity implements FocusCallback {
private GestureDetector gestureDetector;
private nanoStream streamLib = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
streamLib = new nanoStream(new nanoStreamSettings());
if(streamLib.isFocusSupported()) {
gestureDetector = new GestureDetector(this, new GestureListener());
}
...
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)
{
if (gestureDetector != null)
{
gestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
}
return true;
}
....
private class GestureListener implements OnGestureListener {
@Override
public boolean onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e)
{
if (streamLib != null)
{
streamLib.setFocusArea(300, 300, 1f, (int) e.getX(), (int) e.getY(), surface.getWidth(), surface.getHeight(), 1000);
}
return true;
}
@Override
public void onLongPress(MotionEvent e)
{
if (streamLib != null)
{
streamLib.setFocusLockArea(300, 300, 1f, (int) e.getX(), (int) e.getY(), surface.getWidth(), surface.getHeight(), 1000);
}
}
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(Rect rect, Boolean aBoolean) {
Log.i(TAG, "focus success");
}
@Override
public void onFailure() {
Log.i(TAG, "focus failed");
}
}
DeviceProperties
Before Android 4.3 there was no obligation for Android hardware manufacturers to pass the video related parts of the CTS (Compatibility Test Suite). Therefore some Android 4.1 and 4.2 Devices show non standard behaviour in regard to color format definitions and representation of video frames in memory. This could lead to issues in the video stream like switched red and blue colors, dislocated color components or a green bar at the bottom of the video frame. nanoStream Android now provides the functionality to detect and compensate common issues related to this.
Description
nanoStream.getDeviceProperties() is a static function that is running a test on the device hardware to detect non standard behaviour and returning a DeviceProperties object containing the result.
DeviceProperties.getFlags() returns the test result as an integer value that can be stored in the application preferences, to avoid running the device test on every app start.
DeviceProperties can be applied to a new nanoStream instance by calling nanoStream.setDeviceProperties(DeviceProperties).
We recommend to call getDeviceProperties() in a background thread during the first app start on a pre 4.3 device, because the call is blocking and might last up to 5 seconds on older/weaker devices.
We also recommend to store the OS version in the preferences, to be able to detect OS updates and to eventually rerun the device test or stop setting the DeviceProperties if the new OS is 4.3 or higher.
Implementation Example
public class App extends Application
{
private static DeviceProperties deviceProp = null;
public void onCreate()
{
super.onCreate();
Thread chkThread = new Thread(new Runnable()
{
@Override
public void run()
{
try
{
SharedPreferences prefs = PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPreferences(getApplicationContext());
int curApiVer = android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT;
int curAppVer = getPackageManager().getPackageInfo(getPackageName(), 0).versionCode;
int curEncVer = DeviceProperties.VERSION;
int oldApiVer = prefs.getInt("Pref_Android_API", 0);
int oldAppVer = prefs.getInt("Pref_App_Version", 0);
int oldChkVer = prefs.getInt("Pref_Check_Version", 0);
int oldChkResult = prefs.getInt("Pref_Check_Result", -1);
if (((oldApiVer * oldAppVer * oldApiVer) == 0)
|| (oldApiVer < curApiVer)
|| (oldAppVer < curAppVer)
|| (oldChkVer < curEncVer)
|| oldChkResult < 0)
{
Editor edit = prefs.edit();
edit.putInt("Pref_Android_API", curApiVer);
edit.putInt("Pref_App_Version", curAppVer);
/* Run device check */
try
{
deviceProp = nanoStream.getDeviceProperties();
edit.putInt("Pref_Check_Result", deviceProp.getFlags());
edit.putInt("Pref_Check_Version", deviceProp.getVersion());
edit.commit();
}
catch (RuntimeException e)
{
Log.d("Device Check failed", e.toString());
edit.putInt("Pref_Check_Result", -1);
edit.putInt("Pref_Check_Version", 0);
edit.commit();
}
}
else
{
deviceProp = new DeviceProperties(oldChkResult);
}
Log.d("Device Properties: ", deviceProp.toString());
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Log.d(this.getClass().getName(), "Device Check Runnable");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < 18)
{
chkThread.start();
}
...
}
public static DeviceProperties getDeviceProperties()
{
return deviceProp;
}
}
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements NanostreamEventListener
{
...
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
try
{
nanoStreamSettings nss = new nanoStreamSettings();
streamLib = new nanoStream(nss);
DeviceProperties deviceProperties = App.getDeviceProperties();
if(null != streamLib && null != deviceProperties)
{
streamLib.setDeviceProperties(deviceProperties);
}
}
catch(NanostreamException en)
{
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), en.toString(), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
...
}
}